Continuous Deployment (CD)
What is Continuous Deployment?
Continuous Deployment in SAFe encompasses the automated deployment of solutions through various environments, from development to production. It ensures reliable, repeatable, and rapid deployment processes that maintain solution quality and enable quick feedback loops.
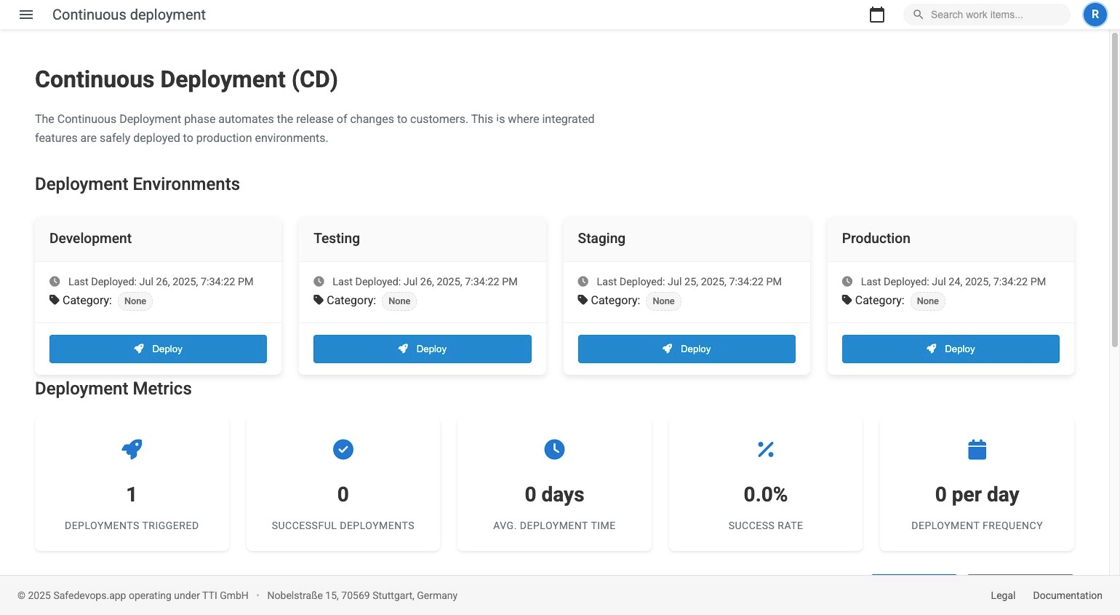
CD Deployment Dashboard
The Continuous Deployment dashboard provides comprehensive visibility into your deployment pipeline, environment status, and deployment metrics across all environments.
Key CD Activities
- Deployment Coordination: Plan and schedule deployments across environments
- Environment Management: Track status and readiness of deployment environments
- Release Validation: Coordinate testing and validation activities in target environments
- Deployment Tracking: Monitor deployment progress and status across the pipeline
- Rollback Planning: Coordinate recovery procedures from deployment issues
CD Deployment Board
Deployment Pipeline Columns
Purpose: Integrated features ready for deployment
Criteria:
- All integration tests passed
- Feature readiness verified
- Deployment package prepared
- Environment dependencies resolved
Purpose: Active deployment processes
Criteria:
- Deployment pipeline executing
- Environment provisioning in progress
- Deployment validation running
- Monitoring systems active
Purpose: Successfully deployed features
Criteria:
- Deployment completed successfully
- Smoke tests passed
- Monitoring confirms health
- Ready for user access
Deployment Flow
Environment Management
Deployment Environments
Standard Environment Pipeline
🔧 Development Environment
ActivePurpose: Initial integration and development testing
- Frequent deployments (multiple times per day)
- Feature branch deployments
- Development team testing
- Minimal data and security constraints
🧪 Testing Environment
ActivePurpose: Comprehensive testing and quality assurance
- System integration testing
- Performance and load testing
- User acceptance testing
- Test data management
🎭 Staging Environment
ActivePurpose: Production-like validation and final testing
- Production data simulation
- Final integration validation
- Stakeholder demonstrations
- Deployment rehearsal
🌟 Production Environment
ActivePurpose: Live customer-facing deployment
- Customer access
- Full monitoring and alerting
- High availability requirements
- Security and compliance controls
CD Metrics and Analytics
Key CD Metrics
Deployment Performance
- Deployments Triggered: Total number of deployment attempts
- Successful Deployments: Deployments completed without issues
- Deployment Success Rate: Percentage of successful deployments
- Average Deployment Time: Time from trigger to completion
- Deployment Frequency: Number of deployments per time period
Quality and Reliability
- Failed Deployments: Deployments that failed or were rolled back
- Mean Time to Recovery (MTTR): Time to restore service after issues
- Change Failure Rate: Percentage of deployments causing production issues
- Lead Time for Changes: Time from code commit to production
Environment Health
- Environment Uptime: Availability of deployment environments
- Resource Utilization: CPU, memory, and storage usage
- Performance Metrics: Response times and throughput
- Security Compliance: Security policy adherence
Automated Deployment Pipeline
Pipeline Stages
| Stage | Activities | Validation | Duration |
|---|---|---|---|
| Build | Code compilation, dependency resolution | Build success, artifact creation | 5-15 minutes |
| Test | Unit tests, integration tests, security scans | All tests pass, security checks clear | 10-30 minutes |
| Package | Container creation, artifact packaging | Package integrity, version tagging | 2-10 minutes |
| Deploy | Environment provisioning, application deployment | Deployment success, health checks | 5-20 minutes |
| Verify | Smoke tests, integration validation | All verifications pass | 5-15 minutes |
Pipeline Configuration
Calendar Integration and Deployment Events
Deployment Scheduling
- Automated calendar event creation for deployments
- Team notification for scheduled deployments
- Deployment window management
- Stakeholder communication and coordination
- Historical deployment tracking
Deployment Event Management
- Event Creation: Automatic calendar events for triggered deployments
- Team Coordination: Multi-team deployment coordination
- Stakeholder Notification: Automated updates to relevant stakeholders
- Deployment Windows: Scheduled maintenance and deployment periods
- Rollback Events: Coordination of rollback activities when needed
Using CD in Safedevops
Getting Started
Deployment Management
- Environment Triggers: Deploy to specific environments with confirmation dialogs
- Status Tracking: Real-time visibility into deployment progress
- Calendar Events: Automatic scheduling and team coordination
- Metrics Dashboard: Comprehensive deployment health monitoring
- Rollback Support: Quick rollback capabilities for failed deployments
Best Practices for CD
For DevOps Engineers
- Implement infrastructure as code for consistent environments
- Use blue-green deployments for zero-downtime releases
- Maintain comprehensive monitoring and alerting
- Automate rollback procedures for quick recovery
- Implement proper security scanning and compliance checks
For Release Managers
- Coordinate deployment schedules across teams
- Ensure proper change management processes
- Communicate deployment status to stakeholders
- Manage deployment dependencies and sequencing
- Track and report on deployment metrics
for Operations Teams
- Monitor production environments continuously
- Maintain runbooks for common deployment scenarios
- Ensure backup and recovery procedures are tested
- Collaborate with development teams on deployment issues
- Optimize environment performance and capacity
Common CD Challenges
Deployment Issues
- Environment Drift: Inconsistencies between environments
- Configuration Errors: Incorrect environment configurations
- Dependency Conflicts: Version mismatches and compatibility issues
- Resource Constraints: Insufficient environment resources
- Security Vulnerabilities: Security issues in deployment pipeline
Solutions and Mitigations
| Challenge | Impact | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Manual Deployment Process | Slow, error-prone deployments | Full automation with CI/CD pipelines |
| Environment Inconsistency | Deployment failures, hard-to-reproduce issues | Infrastructure as code, containerization |
| Long Deployment Times | Delayed releases, increased risk | Pipeline optimization, parallel processing |
| Poor Rollback Capabilities | Extended downtime during issues | Automated rollback, blue-green deployments |
Advanced CD Features
Deployment Strategies
- Blue-Green Deployment: Zero-downtime deployments with environment switching
- Canary Releases: Gradual rollout to subset of users
- Rolling Deployments: Sequential updates across server instances
- Feature Toggles: Control feature visibility without deployment
Security and Compliance
- Security Scanning: Automated vulnerability assessment
- Compliance Checks: Regulatory requirement validation
- Access Controls: Role-based deployment permissions
- Audit Trails: Complete deployment activity logging
Monitoring and Observability
Integration with External Tools
CI/CD Platforms
- Jenkins: Enterprise automation and orchestration
- GitLab CI/CD: Git-integrated continuous deployment
- Azure DevOps: Microsoft ecosystem deployment
- AWS CodePipeline: Cloud-native deployment automation
Infrastructure Tools
- Kubernetes: Container orchestration and deployment
- Terraform: Infrastructure as code provisioning
- Ansible: Configuration management and automation
- Docker: Application containerization