SAFe Continuous Delivery Pipeline
What is the SAFe Continuous Delivery Pipeline?
The SAFe Continuous Delivery Pipeline represents the flow of value from concept to cash. It provides a structured approach to delivering value continuously through three interconnected stages: Continuous Exploration, Continuous Integration, and Continuous Deployment.
Pipeline Overview in Safedevops
The pipeline view provides a holistic visualization of work items flowing through each stage, enabling teams to understand bottlenecks, track progress, and optimize delivery flow.
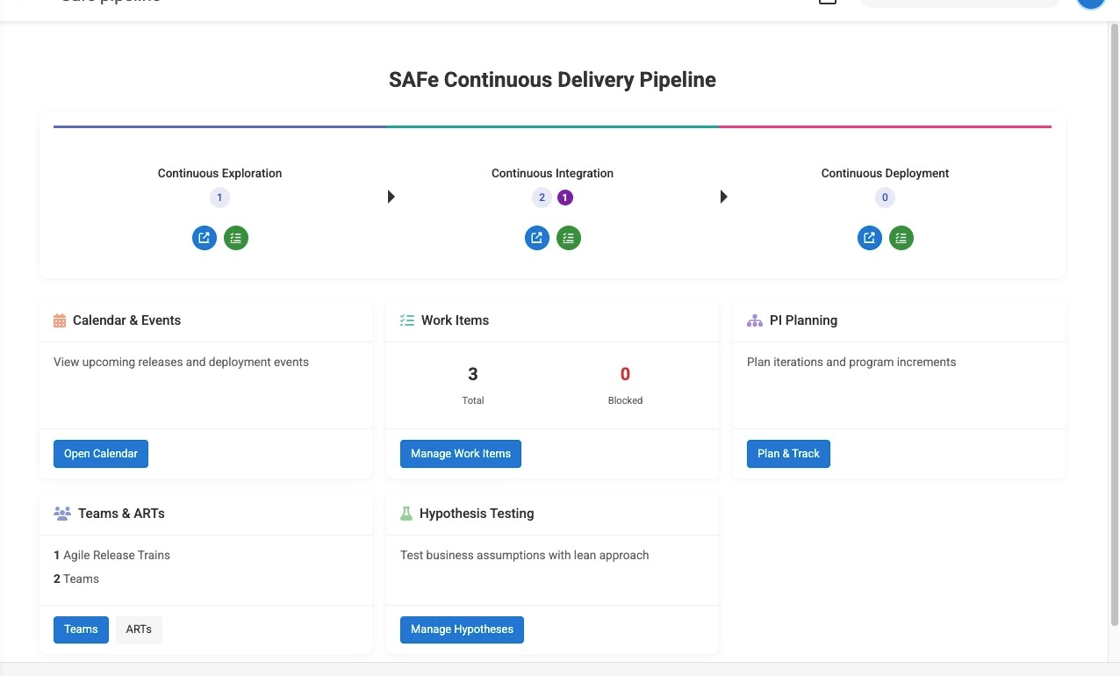
Core Pipeline Principles
- Flow: Optimize for continuous flow of value through the pipeline
- Quality: Build quality in at every stage
- Transparency: Provide visibility into work and progress
- Collaboration: Enable cross-functional collaboration
- Continuous Learning: Learn and adapt based on feedback
Pipeline Stages
Purpose: Hypothesize, collaborate, and architect for features that fulfill customer needs
Key Activities:
- Market and customer research
- Hypothesis development and validation
- Feature definition and prioritization
- Architecture exploration and solution design
Outputs: Ready Features with clear acceptance criteria and architectural guidance
Purpose: Take features and rapidly integrate them into a working solution
Key Activities:
- Feature development and implementation
- Continuous integration of code changes
- Automated testing and quality gates
- System integration and verification
Outputs: Integrated, tested solution ready for deployment
Purpose: Deploy solutions to production environments safely and efficiently
Key Activities:
- Automated deployment pipelines
- Environment management and configuration
- Release validation and smoke testing
- Deployment monitoring and rollback capabilities
Outputs: Solutions deployed to production environments
Pipeline Metrics and Analytics
Flow Metrics
| Metric | Description | Target | Frequency |
|---|---|---|---|
| Lead Time | Time from idea to customer value | Minimize and stabilize | Per feature |
| Cycle Time | Time to complete work once started | Reduce variation | Per work item |
| Throughput | Number of items completed per time period | Steady or increasing | Weekly/Monthly |
| Work in Progress | Active items in each stage | Controlled limits | Real-time |
Quality Metrics
- Defect Density: Defects per feature or story point
- Escaped Defects: Production issues found after release
- Test Coverage: Automated test coverage percentage
- Mean Time to Repair (MTTR): Average time to fix production issues
Using the Pipeline in Safedevops
Navigation and Access
Work Item Flow Management
- Drag and Drop: Move work items between stages using drag and drop
- Status Tracking: Automatic status updates based on stage movement
- Bottleneck Identification: Visual indicators for stages with high WIP
- Flow Optimization: Recommendations for improving flow efficiency
Pipeline Integration
ART and Team Integration
- Multi-Team Coordination: View work from multiple teams in a single pipeline
- ART-level Visibility: Aggregate view across all teams in an ART
- Dependency Management: Track cross-team dependencies within the pipeline
- Resource Allocation: Optimize team assignments based on pipeline load
External Tool Integration
Best Practices
For Release Train Engineers
- Monitor pipeline flow daily and identify bottlenecks
- Facilitate cross-team collaboration and dependency resolution
- Use metrics to drive continuous improvement discussions
- Ensure alignment between pipeline flow and business priorities
For Scrum Masters
- Help teams understand their role in the overall pipeline
- Remove impediments that block pipeline flow
- Encourage teams to optimize for flow, not just velocity
- Facilitate retrospectives focused on pipeline improvements
For Product Owners
- Ensure features are properly prepared before entering CI
- Make prioritization decisions based on pipeline capacity
- Collaborate with teams to maintain steady flow
- Use pipeline data to inform stakeholder communications
Common Challenges and Solutions
Pipeline Bottlenecks
| Challenge | Symptoms | Solutions |
|---|---|---|
| CE Overload | Too many ideas, slow feature definition | Implement WIP limits, improve prioritization |
| CI Congestion | Long integration cycles, frequent conflicts | Smaller batch sizes, more frequent integration |
| CD Delays | Manual deployment processes, environment issues | Automation, infrastructure as code |
| RoD Hesitation | Delayed releases, fear of deployment | Feature toggles, gradual rollouts |
Advanced Pipeline Features
Predictive Analytics
- Flow Forecasting: Predict delivery dates based on historical flow
- Capacity Planning: Optimize team allocation across stages
- Risk Identification: Early warning systems for potential delays
- Trend Analysis: Long-term performance trends and patterns
Automation Capabilities
- Automatic work item transitions based on CI/CD events
- Notification triggers for pipeline stage changes
- Metric collection and dashboard updates
- Integration with external monitoring and alerting systems