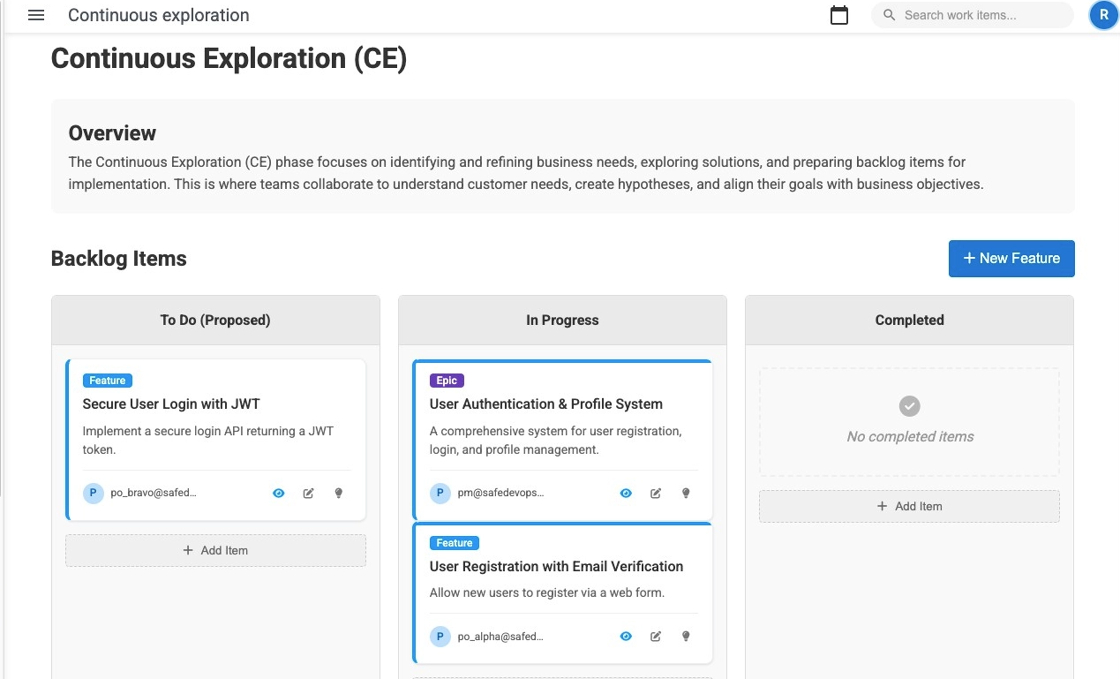
Continuous Exploration (CE)
What is Continuous Exploration?
Continuous Exploration represents the ongoing process of discovering customer needs, market opportunities, and solution approaches. It's where ideas are born, hypotheses are formed, and features are defined with clear business value and acceptance criteria.
CE Dashboard in Safedevops
The Continuous Exploration dashboard provides a Kanban-style view of your exploration backlog, allowing teams to visualize work from initial ideas through completed feature definitions.
Key CE Activities
- Market Research: Understanding customer needs and market opportunities
- Hypothesis Formation: Creating testable assumptions about solutions
- Solution Design: Architectural exploration and technical feasibility
- Feature Definition: Clear specifications with acceptance criteria
- Prioritization: Value-based ordering of exploration items
CE Board and Workflow
Kanban Board Columns
Purpose: New ideas and proposed features awaiting exploration
Criteria:
- Initial business case identified
- Basic user need understood
- Ready for exploration activities
Purpose: Active exploration and refinement activities
Criteria:
- Research and analysis underway
- Hypotheses being tested
- Solution options being evaluated
Purpose: Well-defined features ready for development
Criteria:
- Clear acceptance criteria defined
- Business value articulated
- Technical approach validated
- Ready for Continuous Integration
Work Item Flow
Hypothesis Management
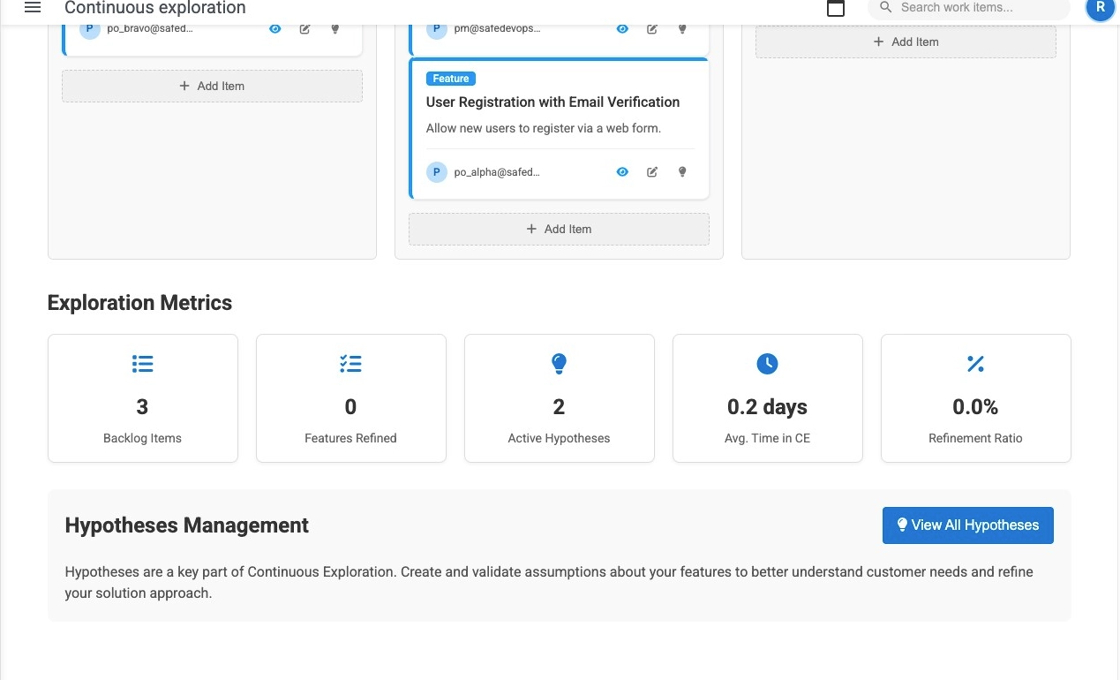
Exploration Metrics and Hypotheses
Track exploration effectiveness with comprehensive metrics and manage hypotheses that drive feature development decisions.
Hypothesis-Driven Development
We believe that [building this feature/capability]
For [target user/customer segment]
Will result in [expected outcome/behavior]
We will know we have succeeded when we see [measurable signal/metric]
Hypothesis Management Features
- Hypothesis Creation: Link hypotheses directly to work items and features
- Test Planning: Define experiments and validation approaches
- Results Tracking: Monitor hypothesis validation outcomes
- Learning Capture: Document insights and pivot decisions
- Stakeholder Communication: Share learnings across teams and ARTs
Hypothesis Lifecycle
| Stage | Activities | Deliverables | Success Criteria |
|---|---|---|---|
| Formation | Identify assumptions, formulate hypothesis | Hypothesis statement | Clear, testable assumption |
| Design | Plan experiments, define metrics | Test plan, success metrics | Measurable validation approach |
| Test | Execute experiments, collect data | Experiment results | Sufficient data for decision |
| Learn | Analyze results, make decisions | Validated learning, next steps | Clear path forward |
CE Metrics and Analytics
Key CE Metrics
Flow Metrics
- Backlog Count: Total number of items in exploration
- Features Refined: Number of features with complete definition
- Time in CE Phase: Average time from idea to feature completion
- Exploration Refinement Ratio: Percentage of refined vs. total features
Quality Metrics
- Hypothesis Count: Number of active hypotheses
- Features with Hypotheses: Features backed by validated hypotheses
- Hypothesis Validation Rate: Percentage of hypotheses tested
- Learning Velocity: Rate of validated learnings per period
Throughput Metrics
- Ideas per Period: New ideas entering the funnel
- Features Completed: Features ready for development
- Conversion Rate: Ideas that become viable features
- Cycle Time: Time from idea to feature readiness
Using CE in Safedevops
Getting Started
Work Item Management
- Creating Items: Add new epics and features to the exploration backlog
- Editing Details: Update descriptions, acceptance criteria, and business value
- Status Updates: Automatic status changes as items move through columns
- Collaboration: Team comments and discussions on work items
Best Practices for CE
For Product Managers
- Start with clear problem statements before jumping to solutions
- Use data and customer feedback to inform hypothesis formation
- Maintain a balanced portfolio of incremental and breakthrough innovations
- Regularly review and prune the exploration backlog
- Engage stakeholders in hypothesis validation activities
For Solution Architects
- Provide technical feasibility input early in the exploration process
- Identify architectural runway needs for upcoming features
- Validate solution approaches through proof of concepts
- Ensure alignment with enterprise architecture guidelines
- Document technical decisions and trade-offs
For UX Designers
- Conduct user research to validate customer needs
- Create low-fidelity prototypes for hypothesis testing
- Design experiments that validate user experience assumptions
- Collaborate with product managers on feature definition
- Ensure accessibility and usability considerations are included
Common CE Challenges
Exploration Bottlenecks
- Analysis Paralysis: Over-analyzing without making decisions
- Feature Factory: Creating features without validating customer needs
- Weak Hypotheses: Assumptions that are not testable or measurable
- Stakeholder Misalignment: Different views on priorities and value
Solutions and Mitigations
| Challenge | Root Cause | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Long Cycle Times | Over-research, perfectionism | Time-box exploration activities, focus on MVP validation |
| Poor Hypothesis Quality | Lack of training, unclear templates | Training on hypothesis formation, use standard templates |
| Limited Customer Input | Insufficient customer access | Establish customer advisory boards, regular feedback sessions |
| Technical Disconnect | Late technical involvement | Include architects in early exploration activities |
Integration with Other Stages
Handoff to Continuous Integration
- Clear feature definition with acceptance criteria
- Validated business case and user value
- Technical approach identified and feasible
- Dependencies mapped and managed
- Team capacity and skills available
Feedback from Later Stages
- Development Insights: Technical learning that informs future exploration
- User Feedback: Post-release feedback that validates or refutes hypotheses
- Market Response: Business metrics that inform future exploration priorities
- Operational Learning: Deployment and scaling insights for architecture
Advanced CE Features
Experiment Management
- A/B Testing Integration: Plan and track feature experiments
- Prototype Management: Version control for design prototypes
- User Research Tools: Survey and interview management
- Analytics Integration: Connect to product analytics platforms
Collaboration Features
- Stakeholder Reviews: Regular review cycles with business stakeholders
- Cross-ART Visibility: Share learnings across multiple ARTs
- Customer Advisory Integration: Direct customer feedback capture
- Market Research Repository: Centralized research findings